Scaling
Contents
Scaling Jobs
HPC by its very nature can use multiple cores and nodes to scale (and speed up a job) by using more processing units.
This is an assumption which can be seriously flawed once we understand the nature of the software and hardware combination.
- This page will look more deeply into this area by splitting the potential issues down:
Memory Bandwidth
When running on many cores with memory access there is only a finite bandwidth of memory access (even with modern memory channels), so acceleration even with a node is not linear and with the effect of false caching; performance can be degraded significantly more.
Node Interconnect Bandwith
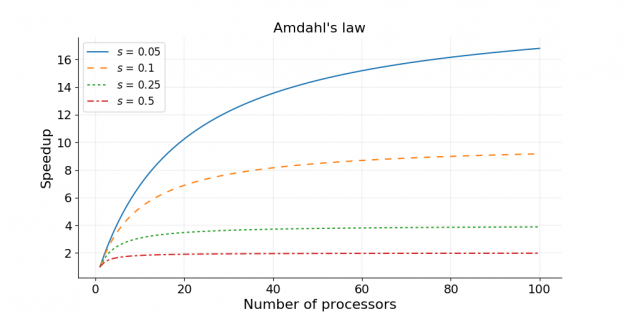
When using MPI across many nodes remember your program needs to send and receive data across the interconnect (the fast network which connects all the nodes together). Again, it is only a very few programs that can scale to a large number of nodes effeciently. Most programs will have a 'sweet spot' (for example 16 nodes), or they will provide very little improvement (< 1% say) for doubling the amount of computing resource deployed to them. In most cases this can only be observed through benchtesting, and is difficult to theoretically calculate.
- s is the amount of time spent in not parallel tasks which could include data transfers like MPI and disk
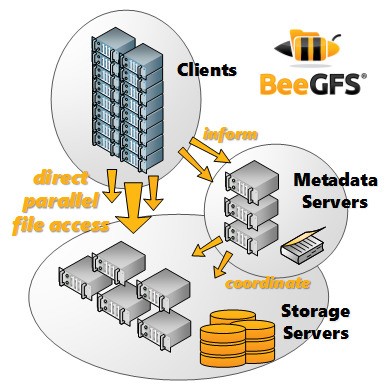
Disk I/O Bandwidth
Programs that generate alot of disk accesses can be magnified when multiple processing cores are being used.
This can be mitigated by using local storage as well.
GPU considerations
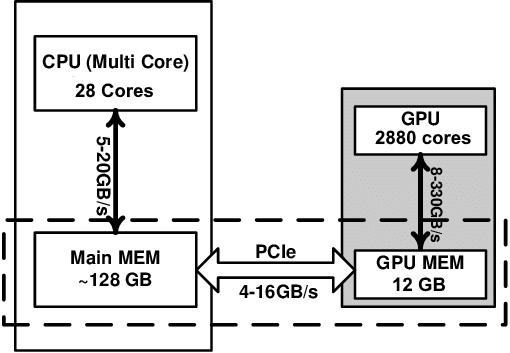
GPU are very good at using the thousands of streaming processors contained with the units, so are ideal for large parallel computations (such as matrix mathematics). However there is a cost of moving data from the CPU memory to GPU memory which is costly in terms of computation time. So, creating the data on the GPU or using large data sets which offset the transfer cost are preferable in terms of a more efficient resource.
- GPU can provide very fast speed-ups; but beware you may find your codes going slower if the problem isn't properly understood.